As a health tourism agency, My Dr Türkiye facilitates access to brain tumor treatments provided by expert medical professionals at accredited healthcare facilities. Brain tumors are abnormal cell growths that can be either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and their type, location, and severity determine the symptoms and treatment approach.
Symptoms of Brain Tumors
Brain tumor symptoms vary based on their size and location, but common signs include:
- Persistent headaches
- Nausea and vomiting
- Changes in vision or hearing
- Seizures
- Difficulty with balance or coordination
- Cognitive or personality changes
Diagnosis of Brain Tumors
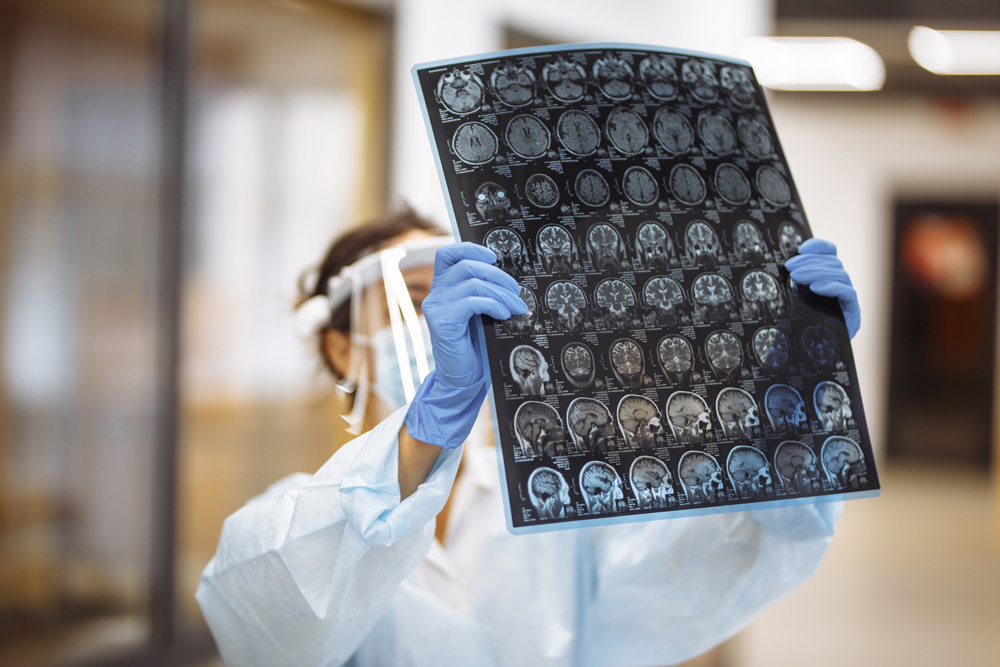
Diagnosing a brain tumor requires a comprehensive medical evaluation, including:
- Neurological exams to assess brain function
- Imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans for detailed brain analysis
- Biopsy procedures to examine tumor cells and determine their nature
Importance of Early Detection
Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for determining the most effective treatment strategy. Specialists develop personalized treatment plans that may involve surgical intervention, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or targeted therapy, depending on the patient’s condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of a brain tumor?
Common symptoms include persistent headaches, nausea, vomiting, changes in vision or hearing, seizures, difficulty with balance or coordination, and cognitive or personality changes. The specific symptoms depend on the tumor’s location and size.
How are brain tumors diagnosed?
Brain tumors are diagnosed through neurological exams, imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans, and sometimes a biopsy to analyze tumor cells. Early diagnosis is critical for effective treatment.
What are the treatment options for brain tumors?
Treatment options depend on the tumor’s type, location, and stage. Common treatments include surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy to target tumor cells, chemotherapy to kill cancer cells, and sometimes targeted therapies or immunotherapy.

